Our bodies are well equipped with most everything we need to survive. Cells are programmed with DNA, take in nutrients from food, and carry out many diverse functions to maintain proper health. Glands produce and secrete hormones at various times of the day and throughout our lifetime which regulate and instruct the cells to perform a specific function.
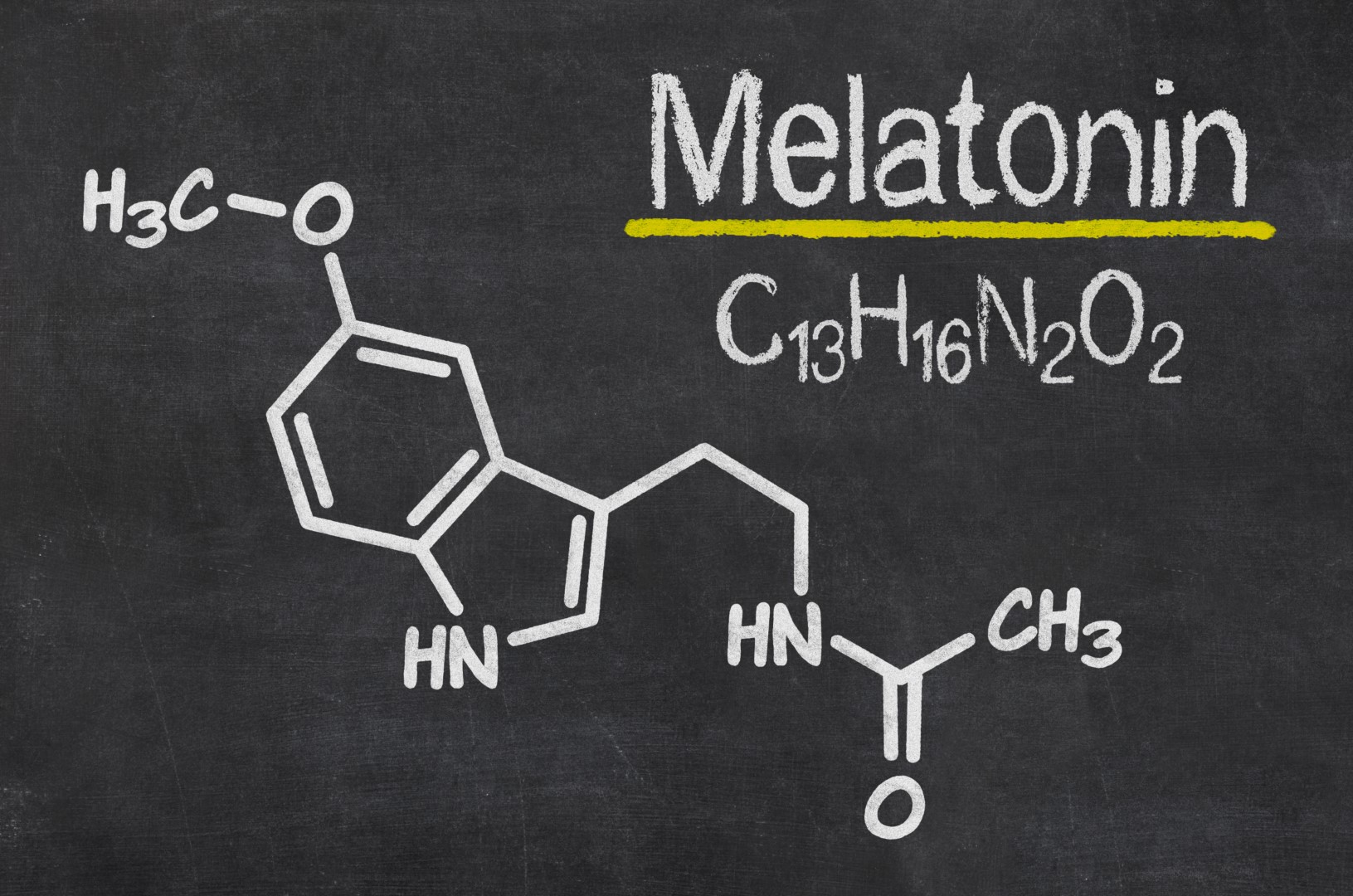
Sometimes, there is a system failure and the glands may not produce the required amount of hormone required to complete a specific task. For example, telling the body it is time for sleep is triggered by melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone produced by the tiny powerhouse called the pineal gland in our brain and sends messages to the body for sleep and awake time.
Under normal circumstances, melatonin is slowly released at sundown as darkness falls triggering our body to relax and prepare for sleep. As morning breaks and light increases, melatonin is no longer produced. Simple? Not quite. Here are some issues if we consider the science:
1) Modern technology creating light-beaming devices used all day and sometimes all night have significantly affected the production of melatonin. The result is a generation with sleep disorders!
2) Shift workers, that is, those who work at night and sleep in the day are at a higher risk of unbalancing the natural production of melatonin. Some will depend on sleep-aids that could prolong the natural production of melatonin as well as have adverse side effects if used over long periods of time.
3) Late nights on a consistent basis will affect the production of this important hormone. Potentially, it could develop into insomnia and affect overall wellness.

4) Jet lag and time zones can temporarily affect the production of melatonin until all body systems settle into the change.
5) Stress appears on every list when it comes to causes of health breakdown. Working long hours and consistently handling deadlines or managing your own business or family dynamics can easily disrupt the production of melatonin.
These are only a few melatonin disruptors, but there is good news! If you think that your body is not producing enough melatonin due to some of the causes mentioned earlier, then you can replace it with certain foods or easy to take supplements at bedtime. Let’s look at these.
1) Best natural food sources of melatonin include bananas, tomatoes, rice, ginger, and barley. Including some of these with an evening meal or as a bedtime snack will add to the production of melatonin. Of course, the famous turkey on whole grain and warm milk snack includes tryptophan which helps produce melatonin!

2) Keep caffeine and heavy greasy meals away from the evening meals as these will only spike the stress hormone production as well as unbalance your blood sugar and keep you from getting a good night’s sleep.
3) Melatonin tablets come in a variety of dosages as well as the melt under your tongue variety. Experts say working your way from a 2mg to 5mg dosage before bedtime can yield some great results. Remember to take them only when you are ready to go to sleep and as a temporary rebalancing of your own melatonin production. Fight the urge to keep reading a book or doing exercise as it will minimize its effects.
Gerry, Your Sleep Expert
See our other blogs with helpful tips on getting better sleep:
Sleep Smarts
How to Improve the Quality of Your Sleep
Hygiene Tips for a Better Sleep
Snack Attack at Bedtime: Easy and Healthy?